Read in : தமிழ்
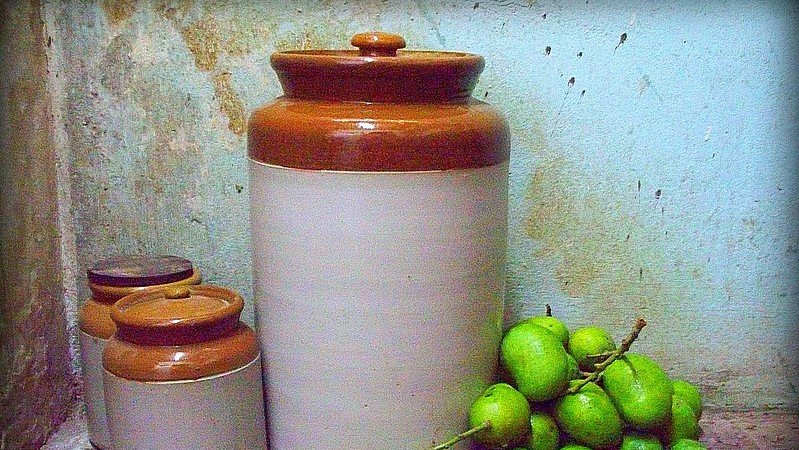
The mention of pickles makes our taste buds mouth- watering. Pickling has been relied upon both to conserve foods and add to their flavour. No Indian meal is complete without a smidgen of pickle. Every Indian household south or North has its distinctive pickles.
In recent times pickles have gained notoriety for their high salt levels. But pickles do offer health benefits.
The word pickle derives its origin from the Dutch word ‘pekel’, meaning ‘brine’. Pickles add spicy flavor and make food palatable to eat. Pickles serve as food flavorings adding desired piquancy through combined action of fruit acid, salt and condiments. Popular Indian pickled foods include wild mangoes, limes, lemons, brinjals ,chillies (and also pork, prawns and fish).
India always had abundant sunshine which enabled Indians to dry their fruits / vegetables in sunshine. The sunshine kills the bacterial spores and molds. By replacing pungency with spiciness, the salt additions to the pickle preparation also increased substantially, making it a villain in the Indian menu. The age old pickle preparatory practices have undergone a change over time. The use of pepper which is a digestive aid was replaced by chilly powder that is an intestinal irritant. The consumption of spicy curries, salted pickles along with junk foods (loaded with salt) could easily add up the daily sodium levels in one’s diet.
The pickle contribution to the Indian menu is substantial as pickling preserves the food to enable use for long periods without refrigeration (hence ideal for long distance journeys). Vegetables and fruits were not commonly through the year, so pickles were the side dish along with rice and chappatis.
Although readymade pickles have made easy the painstaking process of pickle making, in many households, it is an annual ritual that is still treated with the ceremony it rightly deserves. Also, pickling can take even a year for its completion (kaalanimbukaachaar).
Vinegar is used in commercial applications and contains preservatives like EDTA. Vinegar increases the shelf life of the pickles, while in fermentation, which is the traditional method, the food used for pickling produces preservatives all by itself.
When there is sufficient moisture in the food content, dry salt may be used to produce pickling brine. Pickles are made by fermenting vegetables, fruits, or meat in a large amount of salt and oil or vinegar. Other spices may be added to pickles for flavor. The pickling procedure results in the change in the texture of the food and its flavor as well.
The pickle contribution to the Indian menu is substantial as pickling preserves the food to enable use for long periods without refrigeration (hence ideal for long distance journeys). Vegetables and fruits were not commonly available through the year in the past, so pickles were the side dish along with rice and chappatis.
The pickling techniques for the finished product might vary vastly from region to region — Gujarat’s sweet chhunda mango pickle has so little in common with the hot avakkaya pickle from Andhra Pradesh though they are made from the same fruit.
During the pickling process (anaerobic fermentation), the vegetables or fruits are dried, cured with salt in airtight jars and left out in the sun. Salt-tolerant bacteria naturally present on their surface digest the sucrose in the fruit or vegetable matter to produce carbon dioxide, acetic acid and lactic acid. Lactic acid is what gives yogurt its characteristic sourness and imparts a tangy flavour. In the traditional pickling, vegetables and fruits were submerged in brine or salted and shredded. Before transferring the food to vinegar, it may be soaked in brine to reduce moisture content.

(Photo Credit: Indian Pickles by silkrute .com- Flickr)
The acid that is produced acts as a natural preservative and prevents the growth of pathogenic bacteria that could cause the pickle to go rancid. Direct sunlight or adequate ambient light provides the warmth required for the bacteria to go about the business of fermentation. It takes anywhere between 15 days to a month for this process.
Certain precautions need to be taken for a pickle to mature and stay fresh for several years. Most importantly moisture is anathema to pickles. Even the slightest amount of moisture at the time of bottling and even after the pickle is mature can invite mold to form on its surface.
This is why all vegetables and fruits are thoroughly dried before they are cured with salt. It’s also why most Indian pickles are traditionally made in the dry months of summer, when humidity is low and adequate sunlight is available. Using sterile, non-reactive jars and dry ladles, good quality fruits, vegetables and other ingredients and precise proportions of sugar, salt and oil are also important for a pickle to taste right and last long.
In India, oil is a popular medium used for pickling. Pickles in the north of the country are typically made with mustard oil, while the South Indian style is sesame oil. Oil is added to several Indian pickles to increase longevity — it plays the role of the preservative. Oils that stay stable over long periods of time, such as mustard and sesame oil, are preferred.
The herbs and spices that are added to Indian pickles don’t just enhance the taste of the pickle. Many of them have anti-microbial properties that aid in digestion. As days go by, the vegetables tend to leave out water, shrink, at the same time absorb salt. Then all the spices added. The longer the vegetables are soaked, the tender and tastier they become. Finally, heated oil is sprinkled on top of the pickle (with or without tempering). Pickle making doesn’t involve much cooking other than heating the oil.
The spices used bring their own benefits. Cumin and green cardamom are cooling, clove and cinnamon are warming, ginger is good for colds, while raw garlic is good for circulatory ailment. For all the pickle lovers, its worthful to read the Pickle Digest of Usha Prabhakaran, that holds a compendium of over 1,000 pickle recipes from across India.
Certain precautions need to be taken for a pickle to mature and stay fresh for several years. Most importantly moisture is anathema to pickles. Even the slightest amount of moisture at the time of bottling and even after the pickle is mature can invite mold to form on its surface.
In general, pickles should have a pH factor of less than 4.6, which indicates medium to high acidity, sufficient to kill most kinds of bacteria. While pickles made of naturally acidic fruits such as mango and lime don’t require the addition of a souring agent such as vinegar or curd, alkaline vegetables, meat and fish do require a certain level of acidity, which is usually ensured by adding amchur (dried mango powder), vinegar or lime juice.
Given the wide variety of pickles available in India, it’s impossible to fit them into neat categories. One way of organising them could be on the basis of souring agents. Regional cooking in India is influenced by the souring agents that are commonly available in those regions. For instance, amchur is popular in north Indian cuisine, while vinegar is preferred in Goa, and tamarind dominates in the south. Many of these agents are also used in pickling and contribute to the subtle variations in regional styles.
Although not as common, curd or buttermilk is also used as a souring agent in certain south Indian pickles. Sarsaparilla, a creeper with medicinal properties, which is called mahani in Tamil Nadu, is sometimes preserved in buttermilk. Although most pickles can be kept for years if they are stored in the right conditions, there are some that just keep getting better with age. The best known of these is the aged Punjabi pickle made of whole limes, popularly called kala nimbukaachar or kala kagzinimbu. This pickle requires no oil, just ample sunshine.

(Photo Credit: Great Indian Mango Pickle By Madhavi Kuram Flickr)
Though pickle and thokku seem to be similar and are used as condiments, they are prepared in different ways. Thokku calls for some detailed sautéing work to be done, and is generally made with herbs like mint, coriander leaves, or curry leaves etc. Oil is added, and the required ingredient is sauteed till it shrinks and is almost completely devoid of moisture along with chillies and tamarind.
People use brine to make pickles. Brine is water mixed with salt or an acid, such as vinegar. Fermented brine contains good bacteria that may improve health, but only some brines go through the fermentation process. Fermented pickles are full of good bacteria called probiotics, which are important for gut health. Cucumbers are high in an antioxidant called beta-carotene, which the body turns into vitamin A
Understanding the product labels
To get the most benefits from pickles, it is important to know what is in them. People should carefully read the nutrition label while asking the following:
- Only fermented pickles (generally non- vinegar based pickles) offer probiotic benefits, such as a reduced risk of yeast infections and better gut health.
- Vinegar (i.e. Acetic acid) may help control blood sugar.
- Lower sodium foods are a better choice for almost everyone. Lower sodium content also means it is safer to eat more pickles
Pickles offer numerous benefits, since they constitute ingredients made out of raw and unripe ingredients. They act as a rich source of antioxidants. For eg. Swallow root pickle has its antioxidant content kept intact. Antioxidants are the molecules that slow down the process of aging by maintaining the level of oxidants with or without free radical action.
The strong flavour and aroma of pickles activates the salivary glands, and helps in digesting the meal. Pickles were valued for their therapeutic properties. Ayurvedic texts talked about pickles as ‘agnipradeepak’, meaning that they improved the ‘fire’ in your system. By this, they probably meant that the pickles improved metabolism.
Pickles boost immunity, as they constitute vital micronutrients rich in vitamins and minerals which can strengthen the bones, cure anemia, protect vision and so on. Pickles made with leafy vegetables like curry leaves, fenugreek, coriander, mint and spinach supply us significant nutrients like Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and Vitamin K, iron, calcium, and potassium. These nutrients might be missing in our daily diet but the same can be derived through consuming the pickles.
Turmeric forms an important item in the making of the pickle. Turmeric has anti-inflammatory properties that boost your immunity. Pickles made with vinegar help in reducing blood sugar level which in turn improves blood haemoglobin. Acetic acid helps you to maintain your sugar levels. In all, a certain amount of pickle might just be helpful for a lot of diabetic patients.
Since our Indian thali has so much variety we need something that curbs the aftermath of a heavy meal. That is one of the reasons why the pickle has become a part of every meal. Our stomach produces certain probiotic bacteria that help digest our food. Our Indian pickles stimulate the growth of such bacteria which helps to evade digestive problems. If you are a big fan of gooseberry aka amla pickle then you are in for a treat! Gooseberry is alkaline in nature that helps in strengthening and clearing the digestive system.
Liver health can be improved with amla pickle as it contains hepatoprotective properties that protect and makes the liver stronger. You can avoid a lot of liver damage if you have this pickle.
Turmeric forms an important item in the making of the pickle. Turmeric has anti-inflammatory properties that boost your immunity. Pickles made with vinegar help in reducing blood sugar level which in turn improves blood haemoglobin. Acetic acid helps you to maintain your sugar levels. In all, a certain amount of pickle might just be helpful for a lot of diabetic patients.
Pickles serve as a cure to get over a hangover. They help in replenishing the depleted level of sodium. They also help in rehydration so that your body can absorb water more efficiently.
Side effects and allergies
Pickles are good for health but only when consumed in moderation. Pickles increase the risk of esophageal cancer and gastric cancer, and this is true especially in the case of Asian pickled consumption.
Pickles are high on salt content, increasing the risk of hypertension and heart disease. The main risk of eating pickles is increase in blood pressure. Too much oil can increase cholesterol.
People with health conditions such as diabetes, metabolic disorders, or nutritional imbalances, should talk to a doctor or dietitian before making significant changes to their diet.
Read in : தமிழ்